What Is a Storage Area Network?
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a specialized, high-speed network
that provides block-level network access to storage. SANs are typically
composed of hosts, switches, storage elements, and storage devices that are interconnected
using a variety of technologies, topologies, and protocols. SANs may also span
multiple sites.
SANs are often used to:
- Improve application
availability (e.g., multiple data paths)
- Enhance application performance
(e.g., off-load storage functions, segregate networks, etc.)
- Increase storage utilization
and effectiveness (e.g., consolidate storage resources, provide tiered
storage, etc.), and improve data protection and security.
SANs also typically play an important role in an organization's Business
Continuity Management (BCM) activities.
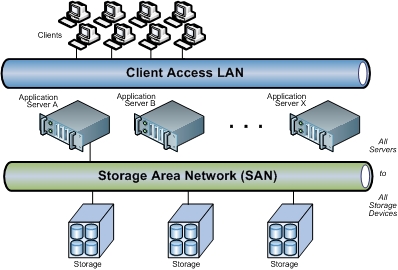
A SAN presents storage devices to a host such that the storage
appears to be locally attached. This simplified presentation of storage to a
host is accomplished through the use of different types of virtualization.
A Storage Area Network (SAN) is a specialized, high-speed network
that provides block-level network access to storage. SANs are typically
composed of hosts, switches, storage elements, and storage devices that are
interconnected using a variety of technologies, topologies, and protocols. SANs
may also span multiple sites.
A SAN presents storage devices to a host such that the storage
appears to be locally attached. This simplified presentation of storage to a
host is accomplished through the use of different types of virtualization.
SANs are often used to:
- Improve application
availability (e.g., multiple data paths)
- Enhance application performance
(e.g., off-load storage functions, segregate networks, etc.)
- Increase storage utilization
and effectiveness (e.g., consolidate storage resources, provide tiered
storage, etc.), and improve data protection and security.
- SANs also typically play an
important role in an organization's Business Continuity Management (BCM)
activities.
A SAN presents storage devices to a host such that the storage
appears to be locally attached. This simplified presentation of storage to a
host is accomplished through the use of different types of virtualization.
SANs are commonly based on Fibre Channel (FC) technology that
utilizes the Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) for open systems and proprietary
variants for mainframes. In addition, the use of Fibre Channel over Ethernet
(FCoE) makes it possible to move FC traffic across existing high speed Ethernet
infrastructures and converge storage and IP protocols onto a single cable.
Other technologies like Internet Small Computing System Interface (iSCSI),
commonly used in small and medium sized organizations as a less expensive
alternative to FC, and InfiniBand, commonly used in high performance computing
environments, can also be used. In addition, it is possible to use gateways to
move data between different SAN technologies.
SNIA is a worldwide source for Vendor Neutral
Storage and Information Management Training & Education
SNIA is a worldwide source for vendor neutral training and
education on Storage and Information Management technologies and provides an
independent understanding of a broad range of Storage and Information
Management technologies from basic foundations to advanced techniques.
SNIA’s impartial educational programs enable the IT professional
to keep abreast of the rapid technology changes in the industry and enable the
community to plan accordingly for the future.




No comments:
Post a Comment